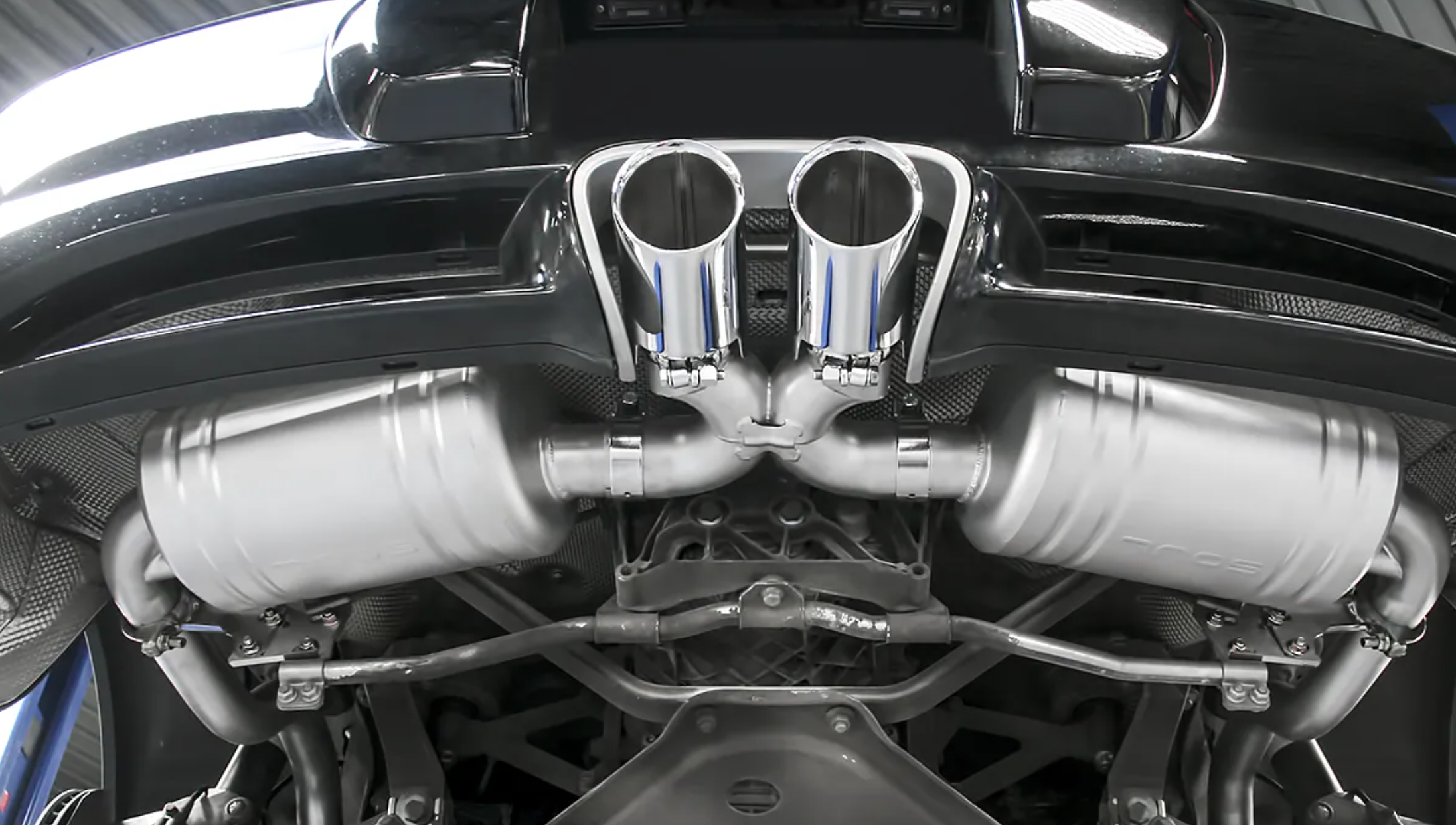
Performance exhaust system – would be the symphony’s brass section if your automobile were an orchestra with the engine acting as the director. A band can perform without brass, of course, but the sound isn’t as clear and deep. In a similar vein, an automobile without a properly adjusted exhaust system can still function, although its efficiency may be significantly reduced. It might be difficult to understand how aftermarket exhaust systems operate since there are a lot of competing theories and viewpoints that obscure the facts. This article will help you select the ideal exhaust system for your car by breaking down how performance exhaust systems operate, emphasizing crucial aspects to think about, going over aftermarket system pricing, and more.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Debate: Zero Back Pressure vs. Necessary Back Pressure

There are two primary schools of thought when it comes to exhaust systems: those who feel that some back pressure is required for optimal performance and others who contend that zero back pressure is preferable. Which is then correct? The type of engine in your car will determine the response.
- Turbocharged Engines: An exhaust system with the least amount of back pressure is optimal for turbocharged engines. As a result, the turbo can spool up more quickly and effectively, increasing power output.
- For naturally aspirated engines, the circumstances are more complex. Two objectives must be balanced in naturally aspirated engines: lowering back pressure to reduce pumping loss (energy loss) and increasing exhaust flow to improve the air-fuel mixture’s intake during the valve overlap period.
Key Functions of Exhaust Systems
Making it simpler for exhaust gasses to leave the engine is the main purpose of an exhaust system. This facilitates more fluid piston movement and lowers pumping loss, the energy needed to release exhaust gasses. Still, it’s not always the case that the “bigger is better” maxim holds true, particularly when it comes to naturally aspirated engines. For these engines to operate at their best, a precise balance is necessary.
Components of an Exhaust System
The idea that the exhaust system is limited to the muffler is a frequent one. In actuality, performance is impacted by every part that is downstream from the cylinder head. These elements consist of:
- Exhaust Manifold (Header): This part directs exhaust gasses into one or more pipes from the engine’s cylinders. Cast iron is commonly used in OEM exhaust manifold construction, which may be hefty and constricting. Switching to aftermarket headers can save weight and increase flow.
- Turbo Manifolds: These manifolds help the turbocharger work by directing exhaust gases to the turbine housing of the turbocharger. Reducing constraints after the turbo boosts power production.
- Downpipe: The downpipe, which is a component of turbocharged cars, transports exhaust gasses from the turbocharger to the remainder of the exhaust system.
- The catalytic converter, mid-pipe (B-pipe), and muffler serve to further direct exhaust gasses toward the back of the car while cutting down on pollution and noise.
Materials Used in Exhaust Systems
Exhaust systems can be made from various materials, each with distinct advantages:
- Mild steel is widely used yet easily corrodes and rusts. Although it costs less, it could not be as durable as other materials.
- Comparing T409 with T304 stainless steel, the former offers moderate corrosion resistance and durability, while the latter offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength due to its higher chromium and nickel content.
- Titanium: Due to its difficulties in manufacturing and machining, titanium is more expensive than other materials. Despite being lightweight and heat-resistant, titanium is a great material for high-performance applications.
Design Considerations: Pipe Diameter and Bending
The performance of an exhaust system is heavily influenced by its design:
- Pipe Diameter: For turbocharged engines, larger diameters generally provide better performance by reducing back pressure. Naturally aspirated engines need carefully tuned pipe diameters to optimize exhaust flow without creating excessive noise.
- Bending Techniques: Exhaust pipes often need to be bent to fit within the vehicle’s chassis. Mandrel bending is preferred over crush bending, as it maintains the pipe’s diameter throughout the bend, ensuring consistent flow.
Types of Aftermarket Exhaust Systems
Aftermarket exhaust systems are categorized based on which parts they replace:
- Cat-Back Exhaust Systems: These systems replace the exhaust components from the catalytic converter to the tailpipe. They are popular for providing enhanced sound and a slight performance boost without extensive modifications.
- Axle-Back Exhaust Systems: These replace the exhaust components from the rear axle to the tailpipe. They are easier to install than cat-back systems and mainly alter the exhaust note.
- Turbo-Back Exhaust Systems: These replace all components from the turbocharger outlet to the tailpipe, providing significant performance gains for turbocharged vehicles.

Noise Levels and Legal Considerations
Exhaust systems can significantly alter the sound of a vehicle. Most countries have regulations limiting exhaust noise to a certain decibel level (e.g., 95 dB in some regions). It’s crucial to ensure that any modifications comply with local noise and emission regulations to avoid legal issues.
Costs of Aftermarket Exhaust Systems
The cost of aftermarket exhaust systems can vary widely based on the type, materials used, and brand. Here is a general breakdown:
- Basic Stainless Steel Systems: $300 – $600
- High-Performance Systems (T304 Stainless or Titanium): $700 – $2,000+
- Custom Fabricated Systems: $1,000 – $5,000+
Choosing the Right Exhaust System for Your Vehicle
Selecting the best exhaust system involves considering your vehicle’s type, your performance goals, and your budget. Start by determining whether you want to enhance sound, increase power, or both. Consulting with local tuners and using resources like this guide can help navigate the various options.
Benefits of Aftermarket Exhaust Systems
Aftermarket exhaust systems offer several benefits:
- Improved Performance: Reduced back pressure and optimized exhaust flow can increase horsepower and torque.
- Enhanced Sound: Many systems are designed to provide a more aggressive exhaust note.
- Weight Reduction: Upgrading from heavy cast iron components to lightweight materials can improve handling and acceleration.
Example: MagnaFlow xMOD Series Performance Exhaust Systems
The xMOD Series Performance Exhaust Systems from MagnaFlow are a great illustration of a high-performance, adaptable solution. Because these systems are modular, power and acoustic qualities may be customized. Their structure is made of stainless steel, which guarantees their longevity and adherence to regulations.
Conclusion
Understanding your vehicle’s requirements, taking the materials and design into account, and adhering to noise and emissions standards are all important when selecting the best performance exhaust system. You may greatly improve the performance and sound of your automobile by carefully choosing an exhaust system that is matched to your engine type and performance objectives. The secret is to strike a balance between practicality and legal compliance and performance improvements, whether you choose an axle-back, cat-back, or complete turbo-back system.